 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
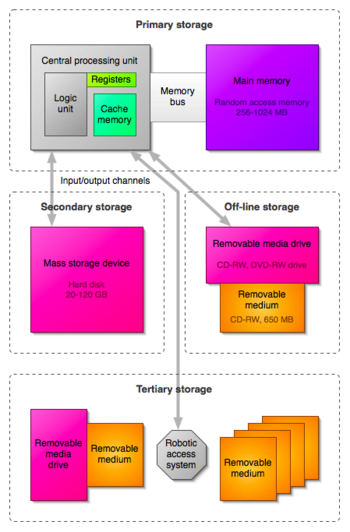
Secondary storage Secondary storage requires the computer to use its
input/output channels to access the information, and is used for long-term
storage of persistent information. However most computer operating systems
also use secondary storage devices as virtual memory - to artificially
increase the apparent amount of main memory in the computer. Secondary
storage is also known as "mass storage", as shown in the diagram
above. Secondary or mass storage is typically of much greater capacity than
primary storage (main memory), but it is also much slower. In modern
computers, hard disks are usually used for mass storage. The time taken to
access a given byte of information stored on a hard disk is typically a few
thousandths of a second, or milliseconds. By contrast, the time taken to
access a given byte of information stored in random access memory is
measured in thousand-millionths of a second, or nanoseconds. This
illustrates the very significant speed difference which distinguishes
solid-state memory from rotating magnetic storage devices: hard disks are
typically about a million times slower than memory. Rotating optical
storage devices, such as CD and DVD drives, are typically even slower than
hard disks, although their access speeds are likely to improve with
advances in technology. Therefore, the use of virtual memory, which is
millions of times slower than "real" memory, significantly
degrades the performance of any computer. Virtual memory is implemented by
many operating systems using terms like swap file or "cache file".
The main historical advantage of virtual memory was that it was much less
expensive than real memory. That advantage is less relevant today, yet
surprisingly most operating systems continue to implement it, despite the
significant performance penalties. Off-line storage is a system where the storage medium can be easily removed from the storage device. Off-line storage is used for data transfer and archival purposes. In modern computers, CDs, DVDs, memory cards, flash memory devices including "USB drives", floppy disks, Zip disks and magnetic tapes are commonly used for off-line mass storage purposes. "Hot-pluggable" USB hard disks are also available. Off-line storage devices used in the past include punched cards, microforms, and removable Winchester disk drums. |